Data Warehouse
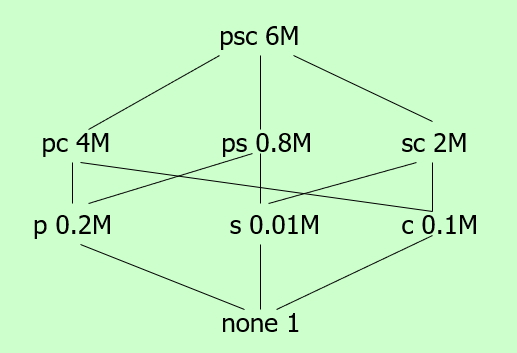
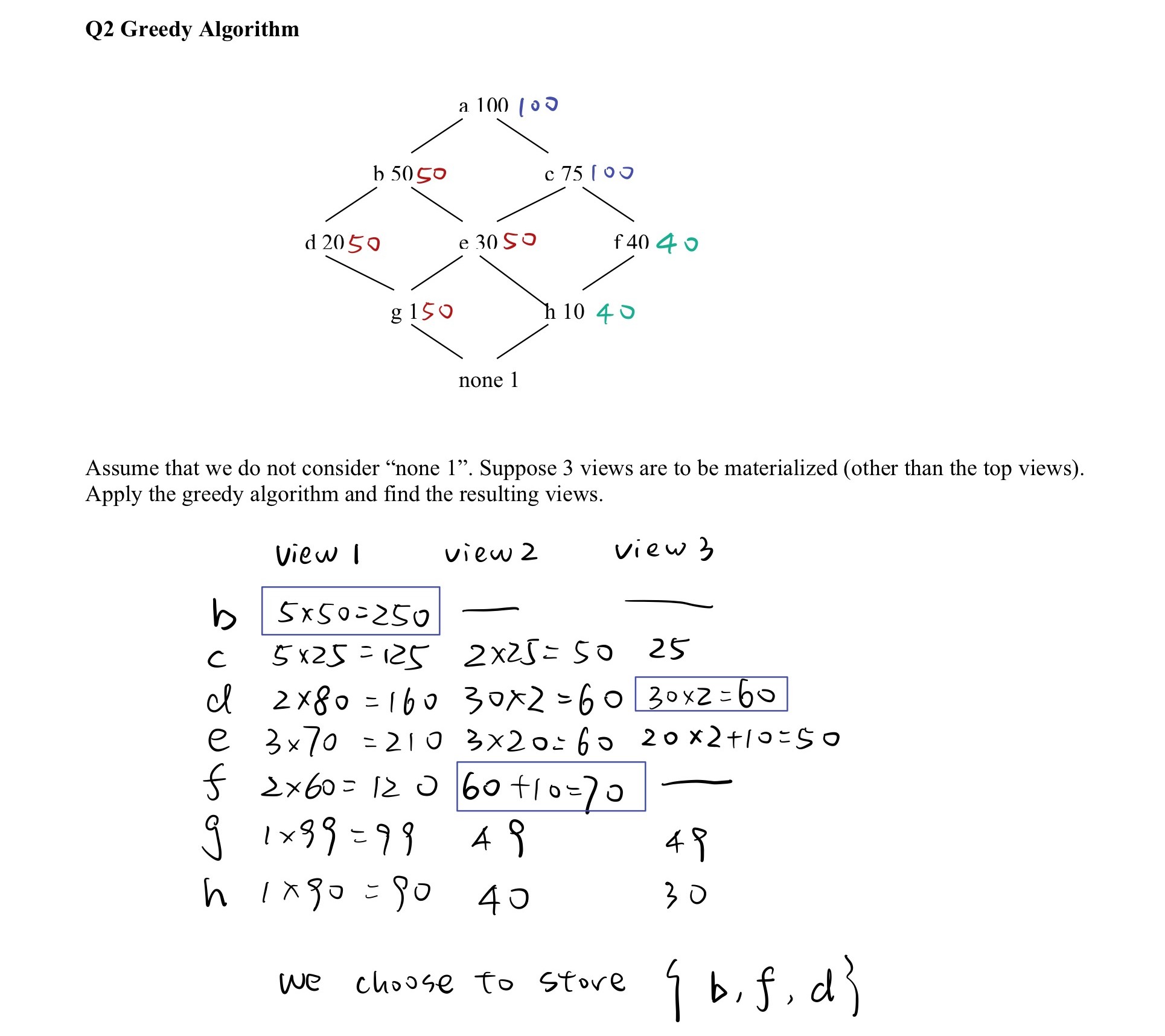
考虑这样一系列视图(view),我们希望存储其中的若干个使得总cost相比于只存储top节点节约的最多。可以使用贪婪算法来处理。
具体而言,每一轮迭代中,对于每个节点,计算储存当前节点所带来的增益,选取增益最大的并进行存储。
ε-deficient synopsis
-
No False Negatives
-
The difference between the estimated frequency and the true frequency is at most εN.
f−f~≤εN
-
All items whose true frequencies less than (s−ε)N are classified as infrequent items in the algorithm output
f~≤(s−ε)N→negative
Sticky Algorithm

以上伪代码为了处理掷骰子部分有点复杂,人话版本:
- 对于每个到来的数据,如果不在内存中,以1/r的概率加入。如果在内存中,count+1
- 每当r变化的时候,对所有内存中的元素做一次删除。具体删除方式为:掷骰子,如果是反面则count -1,如果是正面则停止,如果中途count = 0则删除。
- 最后输出满足f+εN≥sN的元素
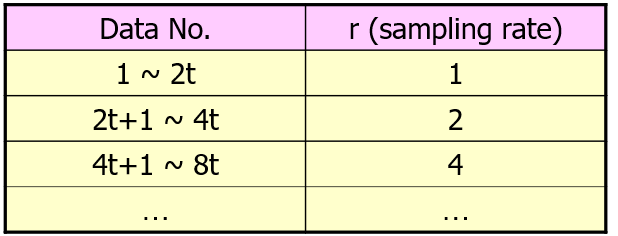
r的确定方式:其中t=1/ε⋅log(s−1δ−1)
Example

Lossy Counting Algorithm

Space Saving Algorithm

Example

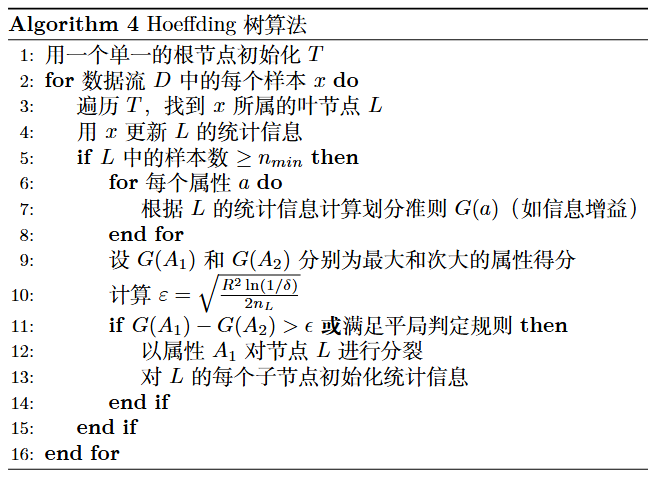
Hoeffding Tree Algorithm
| 样本 |
天气 |
温度 |
是否打球 |
| 1 |
晴 |
热 |
否 |
| 2 |
晴 |
温暖 |
否 |
| 3 |
阴 |
温暖 |
是 |
| 4 |
雨 |
冷 |
是 |
| 5 |
雨 |
冷 |
是 |
| 6 |
雨 |
温暖 |
否 |
| 7 |
阴 |
冷 |
是 |
储存:(feature,attr,label)
比如上述数据集,就要储存样本1:(feature=天气,attr=晴,label=否),样本3:(feature=天气,attr=阴,label=是)等等。然后根据储存的这些数据计算information gain。
例如先读取了前4个数据,则存储应该为
n(feature=天气,attr=晴,label=是)=0n(feature=天气,attr=晴,label=否)=2n(feature=天气,attr=阴,label=是)=1n(feature=天气,attr=阴,label=否)=0n(feature=天气,attr=雨,label=是)=1n(feature=天气,attr=雨,label=否)=0n(feature=温度,attr=热,label=是)=0n(feature=温度,attr=热,label=否)=1n(feature=温度,attr=冷,label=是)=1n(feature=温度,attr=冷,label=否)=1n(feature=温度,attr=温暖,label=是)=1n(feature=温度,attr=温暖,label=否)=0
计算信息增益(假设使用gini index):
G(D)=1−41−41=0.5G(天气)=21⋅0+41⋅0+41⋅0=0G(温度)=41⋅0+21⋅0.5+41⋅0=0.25
以上这些信息增益都可以通过n算出,而无需依赖原表
随后计算Hoeffding Bound。在本例子中R=log22=1,因此
ϵ=2×4ln(1/0.05)≈82.9957≈0.61
我们发现
Gain(天气)−Gain(温度)=0.25<0.61
所以暂时不分裂,以此类推。







